Variation in surface properties, metabolic capping, and antibacterial activity of biosynthesized silver nanoparticles: comparison of bio-fabrication potential in phytohormone-regulated cell cultures and naturally grown plants†
Abstract
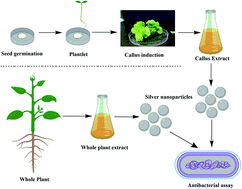
We compared surface properties, metabolic capping and antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles, synthesized through extracts of cell cultures of Fagonia indica and its naturally grown form. Extracts from cell cultures (produced with thidiazuron (TDZ) or melatonin (MLN)) were compared to the naturally grown whole plant extracts (WPEs) for their reducing potential, and their effects on physical and biochemical properties of the biosynthesized silver nanoparticles. UV-Vis spectroscopy revealed that the surface plasmon resonance peaked at λ = 415 nm for MLN-AgNPs, λ = 430 nm for TDZ-AgNPs and λ = 460–465 nm for WPE-AgNPs. Transmission electron microscopy and energy dispersive X-rays of AgNPs showed that compared to WPE-AgNPs (mean diameter = 22 nm), extracts from MLN- and TDZ-induced cell cultures produced particles with spherical shapes and smaller diameters (i.e. mean diameter = 15 nm and 19 nm, respectively). Size distribution analysis also showed that TDZ-AgNPs were nearer to a symmetric distribution in terms of diameter (skewness = 0.80) as compared to WPE-AgNPs (skewness = 0.9) and MLN-AgNPs (skewness = 1.4). Furthermore, MLN-induced cell culture extracts produced AgNPs in higher concentration (210 μg mL−1) compared to AgNPs from TDZ-induced cell culture extracts (160 μg mL−1) and WPE (138 μg mL−1). Two-way comparisons of LC-MS/MS profiles of TDZ-AgNPs, MLN-AgNPs, and WPE-AgNPs revealed differences in their secondary metabolite profiles, which might account for differences in their differential response in bio-fabrication, and size distribution. Activity against different pathogenic bacterial strains, Escherichia coli, Bacillus cereus, Xanthomonas citri, Agrobacterium tumefaciens, Streptomyces griseus, and Erwinia carotovora suggested that MLN-AgNPs were more effective compared to TDZ- and WPE-AgNPs. These results indicated that phytohormones induced cell cultures can enhance the production, physical and biochemical properties of AgNPs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...