Synthesis of aryl azide chain-end functionalized N-linked glycan polymers and their photo-labelling of specific protein†
Abstract
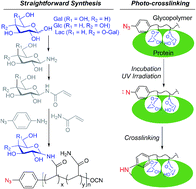
We report a straightforward synthesis of aryl azide chain-end functionalized N-linked glycan polymers and its application for affinity-assisted photo-labelling of specific protein. The aryl azide chain-end functionalized N-glycan polymers, including N-galactosyl, N-glucosyl, and N-lactosyl polymer, were synthesized from free glycan via glycosylamine intermediates followed by acrylation and polymerization via cyanoxyl-mediated free radical polymerization (CMFRP) in a one-pot fashion. The aryl azide chain-end functionalized N-glycan polymers were characterized by 1H NMR and IR spectroscopy. The affinity-assisted photo-labeling capabilities of the aryl azide N-glycan polymers were demonstrated with aryl azide N-lactosyl polymer as a ligand for β-galactose-specific lectin from Arachis hypogaea (PNA) after UV irradiation and confirmed by SDS-PAGE with silver staining. Overall, the aryl azide chain-end functionalized N-linked glycan polymers will be useful multivalent ligands for specific protein labelling and functionality studies.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...