Temperature-responsive iron nanozymes based on poly(N-vinylcaprolactam) with multi-enzyme activity†
Abstract
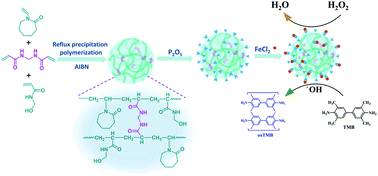
Iron (Fe)-based nanozymes are widely applied in the biomedical field due to their enzyme-like catalytic activity. Herein, Fe(II)-based coordination polymer nanohydrogels (FeCPNGs) have been conveniently prepared as a new type of nanozyme by the chelation reaction between ferrous iron and polymer nanohydrogels. The P(VCL-co-NMAM) nanohydrogels prepared by a reflux precipitation polymerization method using N-vinylcaprolactam (VCL) and N-methylol acrylamide (NMAM) as monomers and N,N-methylenebisacrylamide (MBA) as a crosslinker were esterified using P2O5 and then chelated with Fe(II) ions to form nanozymes with peroxidase and superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity. It was found by dynamic light scattering (DLS) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) that the nanohydrogels prepared with a monomer concentration of 4% and mass ratio of 1 : 1 (VCL : NMAM) had more uniform particle size, better dispersion and a distinct temperature response. The results of Fourier transform infrared (FTIR), DLS, TEM, X-ray powder diffraction (XRD) and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) indicated the successful preparation of the esterified nanohydrogel and FeCPNGs. Of particular importance is that such FeCPNGs can functionally mimic two antioxidant enzymes (peroxidase and superoxide dismutase) by UV analysis of catalytic oxidation between 3,3,5,5-tetramethylbenzidine (TMB) and H2O2 and the kit analysis of SOD-like activity.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...