Synthesis and characterization of a hyaluronic acid-based hydrogel with antioxidative and thermosensitive properties†
Abstract
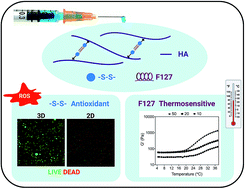
Peripheral arterial disease (PAD) is initiated by progressive atherosclerotic blockages of the arteries supplying the lower extremities. The most common presentation of PAD is claudication (leg pain and severe walking limitation), with many patients progressing to limb threatening ischemia and amputation. Biomaterial approaches are just beginning to be explored in the therapy of PAD with different materials now being evaluated for the delivery of cells or growth factors in animal models of PAD. A biomaterial matrix optimized for minimally invasive injection in the ischemic leg muscles of patients with PAD is urgently needed. There are several important requirements for optimal delivery, retention, and performance of a biomaterial matrix in the mechanically, histologically, and biochemically dynamic intramuscular environment of the PAD leg. Ideally, the material should have mechanical properties matching those of the recipient muscle, undergo minimal swelling, and should introduce properties that can ameliorate the mechanisms operating in PAD like oxidative stress and damage. Here we have developed an injectable, antioxidative, and thermosensitive hydrogel system based on hyaluronic acid (HA). We first synthesized a unique crosslinker of disulfide-modified poloxamer F127 diacrylate. This crosslinker led to the creation of a thermosensitive HA hydrogel with minimal swelling and muscle-matching mechanical properties. We introduced unique disulfide groups into hydrogels which functioned as an effective reactive oxygen species scavenger, exhibited hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)-responsive degradation, and protected cells against H2O2-induced damage. Our antioxidative thermosensitive HA hydrogel system holds great potential for the treatment of the ischemic legs of patients with PAD.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...