Application and interpretation of deep learning methods for the geographical origin identification of Radix Glycyrrhizae using hyperspectral imaging
Abstract
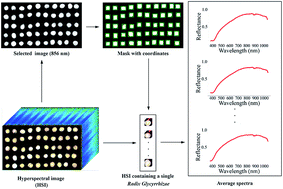
Radix Glycyrrhizae is used as a functional food and traditional medicine. The geographical origin of Radix Glycyrrhizae is a determinant factor influencing the chemical and physical properties as well as its medicinal and health effects. The visible/near-infrared (Vis/NIR) (376–1044 nm) and near-infrared (NIR) hyperspectral imaging (915–1699 nm) were used to identify the geographical origin of Radix Glycyrrhizae. Convolutional neural network (CNN) and recurrent neural network (RNN) models in deep learning methods were built using extracted spectra, with logistic regression (LR) and support vector machine (SVM) models as comparisons. For both spectral ranges, the deep learning methods, LR and SVM all exhibited good results. The classification accuracy was over 90% for the calibration, validation, and prediction sets by the LR, CNN, and RNN models. Slight differences in classification performances existed between the two spectral ranges. Further, interpretation of the CNN model was conducted to identify the important wavelengths, and the wavelengths with high contribution rates that affected the discriminant analysis were consistent with the spectral differences. Thus, the overall results illustrate that hyperspectral imaging with deep learning methods can be used to identify the geographical origin of Radix Glycyrrhizae, which provides a new basis for related research.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...