Detection of xanthine in food samples with an electrochemical biosensor based on PEDOT:PSS and functionalized gold nanoparticles†
Abstract
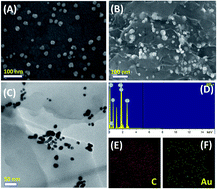
An innovative biosensor assembly relying on glassy carbon electrodes modified with nanocomposites consisting of poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) polystyrene sulfonate (PEDOT:PSS) as a host matrix with functionalized gold nanoparticles (GCE/PEDOT:PSS-AuNPs) is presented for the selective and sensitive detection of xanthine (XA). The developed sensor was successfully applied for the quantification of XA in the presence of significant interferents like hypoxanthine (HXA) and uric acid (UA). Different spectroscopy and electron microscopy analyses were done to characterize the as-prepared nanocomposite. Calibration responses for the quantification of XA was linear from 5.0 × 10−8 to 1.0 × 10−5 M (R2 = 0.994), with a detection limit as low as 3.0 × 10−8 (S/N = 3). Finally, the proposed sensor was applied for the analyses of XA content in commercial fish and meat samples and satisfactory recovery percentage was obtained.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...