Ultrasound-mediated delivery of RGD-conjugated nanobubbles loaded with fingolimod and superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: targeting hepatocellular carcinoma and enhancing magnetic resonance imaging†
Abstract
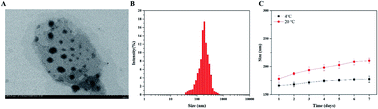
Nanobubbles (NBs) are considered to be a new generation of ultrasound-responsive nanocarriers that can effectively target tumors, accurately release multi-drugs at desired locations, as well as simultaneously perform diagnosis and treatment. In this study, we designed theranostic NBs (FTY720@SPION/PFP/RGD-NBs) composed of RGD-modified liposomes as the shell, and perflenapent (PFP), superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPION), and fingolimod (2-amino-2[2-(4-octylphenyl)ethyl]-1,3-propanediol, FTY720) encapsulated as the core. The prepared FTY720@SPION/PFP/RGD-NBs were black spheres with a diameter range of 160–220 nm, eligible for enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effects. The calculated average drug loading efficiency (LE) and encapsulation efficiency (EE) of the FTY720@SPION/PFP/RGD-NBs were 9.18 ± 0.61% and 88.26 ± 2.31%, respectively. With the promotion of low-intensity focused ultrasound (LIFU), the amount and the rate of FTY720 released from the prepared NB complex were enhanced when compared to the samples without LIFU treatment. In vitro magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) trials showed that the prepared FTY720@SPION/PFP/RGD-NBs had a high relaxation rate and MRI T2-weighted imaging (T2WI) scanning sensitivity conditions. The cell viability studies demonstrated that both HepG2 and Huh7 cells co-cultured with FTY720@SPION/PFP/RGD-NB (100 μg mL−1) + LIFU treatment had the lowest survival rate compared with the other groups at 24 h and 48 h, showing that FTY720@SPION/PFP/RGD-NB had the strongest anti-tumor efficiency among the prepared NBs. The cytotoxicity study also demonstrated that the prepared NBs had low toxicity to normal fibroblast 3T3 cells. Cellular uptake studies further indicated that both LIFU treatment and RGD modification could effectively improve the tumor-targeted effects, thereby enhancing the antitumor efficacy. The qRT-PCR results indicated that LIFU-mediated FTY720@SPION/PFP/RGD-NB could significantly cause the activation of Caspase3, Caspase9 and p53 compared to the control group, inducing HepG2 apoptosis. These results together indicated that FTY720@SPION/PFP/RGD-NBs combined with LIFU may serve as a multifunctional drug delivery platform for hepatocellular carcinoma treatment and provide a new strategy for tumor visualization by MRI.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...