Short peptides conjugated to non-peptidic motifs exhibit antibacterial activity
Abstract
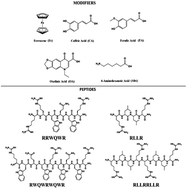
Short peptides derived from buforin and lactoferricin B were conjugated with other antimicrobial molecules of different chemical natures. The sequences RLLR, RLLRLLR, RWQWRWQWR, and RRWQWR were conjugated at their N-terminal end with non-peptidic molecules such as 6-aminohexanoic acid, ferrocene, caffeic acid, ferulic acid, and oxolinic acid. Peptide conjugates and unmodified peptides were synthesized by means of solid-phase peptide synthesis using the Fmoc/tBu strategy (SPPS-Fmoc/tBu), purified via RP-SPE, and characterized via RP-HPLC and MS. The peptides' antibacterial activity against bacterial strains E. coli ATCC 25922 and S. aureus ATCC 25923 was evaluated, and the results showed that the peptide conjugates exhibited higher antibacterial activity than the original unconjugated peptides. Conjugation of AMPs is a promising strategy for designing and identifying new drugs for treating bacterial infections.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...