Selective determination of Ag+ in the presence of Cd2+, Hg2+ and Cu2+ based on their different interactions with gold nanoclusters†
Abstract
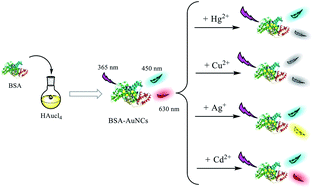
In this work, a fluorescence method was developed for selective detection of Ag+ in the presence of Cd2+, Hg2+, and Cu2+ based on gold nanoclusters (AuNCs). That is, bovine serum albumin (BSA) templated AuNCs with double emission peaks were synthesized using BSA as a protective agent. AuNCs with uniform distribution and average size between 2.0 and 2.2 nm were synthesized using a green and simple method, and showed bright orange-red fluorescence under ultraviolet light. AuNCs have two emission peaks at 450 nm and 630 nm with an excitation wavelength of 365 nm. Under alkaline conditions, Cd2+ can combine with the surface sulfhydryl groups of BSA–AuNCs to form Cd–S bonds, which cause AuNCs to aggregate, resulting in an increase in fluorescence intensity at 630 nm. Conversely, due to the d10–d10 metal affinity interaction, the addition of Hg2+ can reduce the fluorescence peak at 630 nm. Ag+ was reduced to Ag0 by gold nuclei in AuNCs, forming a stable hybrid Au@ AgNCs species with blue-shifted and enhanced fluorescence. Finally, the paramagnetic behavior of Cu2+ combined with BSA causes the excited electrons of the gold cluster to lose their energy via ISC, eventually leading to simultaneous quenching of the two emission peaks. The results show that the limit of detection (LOD) of Ag+, Hg2+, Cd2+ and Cu2+ is 1.19 μM, 3.39 μM, 1.83 μM and 5.95 μM, respectively.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...