Synthesis of a novel arginine-modified starch resin and its adsorption of dye wastewater
Abstract
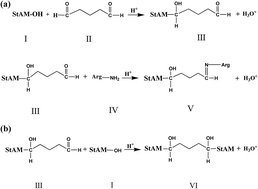
In this work, corn starch (St) was firstly grafted with polyacrylamide (PAM) to obtain StAM, which was subsequently immobilized with arginine to obtain a guanidine-containing starch-based resin, StAM–Arg. The synthesized products were characterized via Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), 13C-NMR nuclear magnetic resonance (13C-NMR), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), gel permeation chromatography (GPC), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA). StAM–Arg exhibited a significantly enhanced adsorption capacity for acid fuchsin (AF), acid orange G (AOG), and acid blue 80 (AB80) compared with zeolite, diatomite, St and StAM, and it also exhibited broad-spectrum adsorption for different dyes. Weak acidic conditions were favorable for the resin to adsorb acid dyes. The decolorization rate (DR) by StAM–Arg for mixed wastewater reached 82.49%, which was higher than that of activated carbon (DR = 58.09%). StAM–Arg showed high resistance to microbial degradation, resulting in significantly improved structural stability for the resin. Its antibacterial rate (AR) for E. coli was up to 99.73%. After 7 days in simulated natural water, the weight loss ratio (WR) of StAM–Arg was 14.5%, which was much lower than that of St (WR = 66.53%). The introduced guanidine groups were considered to be the major reason for the observed improvements. Furthermore, the cationic guanidine could trap the acid dyes via ion-exchange reactions, while effectively inhibiting or eliminating the growth of bacteria on the adsorbent surface. The above advantages, including good dyestuff adsorption properties, high structural stability and prolonged service life, make StAM–Arg overcome the inherent drawbacks of the existing natural polymer adsorbents and have good application prospect in the treatment of textile wastewater.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...