Multi-omics based characterization of antibiotic response in clinical isogenic isolates of methicillin-susceptible/-resistant Staphylococcus aureus†
Abstract
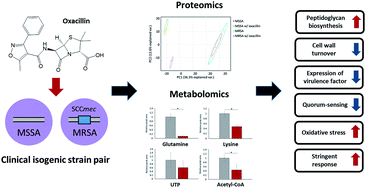
As demands for new antibiotics and strategies to control methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) increase, there have been efforts to obtain more accurate and abundant information about the mechanism of the bacterial responses to antibiotics. However, most of the previous studies have investigated responses to antibiotics without considering the genetic differences between MRSA and methicillin-susceptible S. aureus (MSSA). Here, we initially applied a multi-omics approach into the clinical isolates (i.e., S. aureus WKZ-1 (MSSA) and S. aureus WKZ-2 (MRSA)) that are isogenic except for the mobile genetic element called staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec (SCCmec) type IV to explore the response to β-lactam antibiotics (oxacillin). First, the isogenic pair showed a similar metabolism without oxacillin treatment. The quantitative proteomics demonstrated that proteins involved in peptidoglycan biosynthesis (MurZ, PBP2, SgtB, PrsA), two-component systems (VrsSR, WalR, SaeSR, AgrA), oxidative stress (MsrA1, MsrB), and stringent response (RelQ) were differentially regulated after the oxacillin treatment of the isogenic isolates. In addition, targeted metabolic profiling showed that metabolites belonging to the building blocks (lysine, glutamine, acetyl-CoA, UTP) of peptidoglycan biosynthesis machinery were specifically decreased in the oxacillin-treated MRSA. These results indicate that the difference in metabolism of this isogenic pair with oxacillin treatment could be caused only by SCCmec type IV. Understanding and investigating the antibiotic response at the molecular level can, therefore, provide insight into drug resistance mechanisms and new opportunities for antibiotics development.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...