Impact of drying/wetting conditions on the binding characteristics of Cu(ii) and Cd(ii) with sediment dissolved organic matter
Abstract
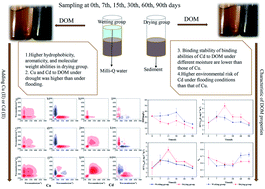
The biogeochemical processing of dissolved organic matter (DOM) in bottomland sediment under drying/wetting conditions regulates the environmental behavior of heavy metals. Although moisture is a critical factor, the structural characteristics of DOM and its reactivity with heavy metals under drying/wetting conditions are not well known. Herein, the response of DOM to drying/wetting conditions and its influence on the binding of Cu(II) and Cd(II) onto DOM were clarified via various multi-spectroscopic techniques. Ultraviolet-visible spectra (UV-Vis) showed that higher aromatic, hydrophobic, and molecular weight fractions were observed in sediment DOM under drying conditions than those under wetting conditions. The binding abilities for Cd(II) with DOM under drying/wetting conditions are lower than those for Cu(II). The stability constants between Cu(II) and DOM were found to decrease under drying/wetting conditions; however, the binding capacities for Cu(II) increased, especially under wetting conditions. Two-dimensional correlation spectroscopy based on Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) and synchronous fluorescence spectra (SFS) showed that Cu(II) and Cd(II) have different binding sequences and binding sites and that Cu(II) has more binding sites under drying and wetting conditions; however, Cd(II) shows the opposite behavior. These results clearly demonstrate that the binding of sediment DOM with Cu(II) is more prevalent and stable compared with Cd(II) under drying and wetting conditions. Because of its relatively low binding capacity and binding stability, Cd(II) can exhibit a high environmental hazard for migration and transformation with DOM due to water flow under wetting conditions. This study helps reveal the impact of drying/wetting conditions on the environmental behavior of heavy metals in bottomland wetlands.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...