Efficient Ce–Co composite oxide decorated Au nanoparticles for catalytic oxidation of CO in the simulated atmosphere of a CO2 laser†
Abstract
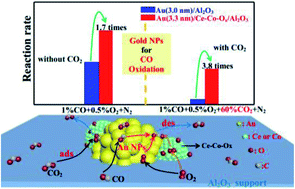
Gold nanoparticles have a high activity for CO oxidation, making them suitable to be used in a CO2 laser which maintains its efficiency and stability via the recombination of CO and O2 produced by the CO2 decomposition. However, the high concentration of CO2 in the working environment greatly reduces the activity of the catalyst and makes the already unstable gold nanoparticles even more so. A novel Au/Ce-Co-Ox/Al2O3 gold catalyst, prepared by a deposition precipitation method in this study, displays high activity and good stability for CO oxidation in a simulated atmosphere of a CO2 laser with the feed gases containing a high concentration of CO2 up to 60 vol% but a low concentration of O2 for the stoichiometric reaction with CO. An excellent performance for CO oxidation under CO2-rich conditions could be achieved by decorating the surface of the Al2O3 support with Ce–Co composite oxides. The strong interaction between gold and the composite support, accompanied by the increase of labile lattice oxygen species and the decrease of surface basicity, led to a high CO oxidation rate and resistance towards CO2 poisoning.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...