Simple weak-acid derivatives of paclitaxel for remote loading into liposomes and improved therapeutic effects†
Abstract
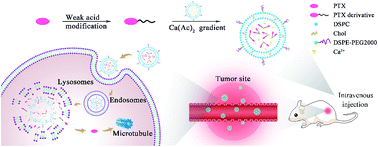
Liposomes are among the most successful nanocarriers; several products have been marketed, all of which were prepared by active loading methods. However, poorly water-soluble drugs without ionizable groups are usually incorporated into the lipid bi-layer of liposomes by passive loading methods, with serious drug leakage during blood circulation. Furthermore, there have been few improvements in their anti-cancer activity and safety. Herein, we designed and synthesized three weak-acid modified paclitaxel (PTX) derivatives with a one-step reaction for the remote loading of liposomal formulations. By comparison, PTX-succinic acid liposomes (PTX-SA LPs) exhibited the highest encapsulation efficiency (97.2 ± 1.8%) and drug loading (8.84 ± 0.16%); meanwhile, there was almost no change in their particle size or zeta potential within one month. Furthermore, compared with Taxol®, the PTX-SA LPs showed a 4.35-fold prolonged half-time, enhanced tumor accumulation, and an increased maximum tolerated dose (MTD) of more than 30 mg kg−1. As a result, the PTX-SA LPs displayed significantly improved in vivo anti-cancer efficacy in comparison with Taxol®. Therefore, weak-acid modification is proved to be a simple and effective method to achieve remote loading and high encapsulation efficiency of poorly soluble drugs, showing great potential for clinical application.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...