Mechanism analysis of Au, Ru noble metal clusters modified on TiO2 (101) to intensify overall photocatalytic water splitting
Abstract
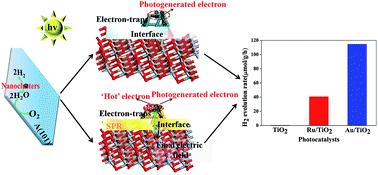
Accelerating the separation and migration of photo-carriers (electron–hole pairs) to improve the photo-quantum utilization efficiency in photocatalytic overall water splitting is highly desirable. Herein, the photo-deposition of Ru or Au noble metal clusters with superior electronic properties as a co-catalyst on the (101) facet of anatase TiO2 and the mechanism of intensifying the photocatalysis have been investigated by calculation based density functional theory (DFT). As a result, the as-synthesized Ru/TiO2 and Au/TiO2 exhibit high hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) activity. Such a greatly enhanced HER is attributed to the interfacial interactivity of the catalysts due to the existence of robust chemical bonds (Ru–O–Ti, Au–O–Ti) as electron-traps that provide the photogenerated electrons. In addition, the formation of new degenerate energy levels due to the existence of Ru-4d and Au-5d electronic impurity states leads to the narrowing of the band gap of the catalysts. In addition, the as-synthesized Au/TiO2 exhibits more faster HER rate than Ru/TiO2, which is attributed to the effects of surface plasmon resonance (SPR) as a synergistic effect of plasmon-induced ‘hot’ electrons that enhance the harvesting of the final built-in electric field and promote the migration and separation of the photo-carriers, which efficiently facilitates hydrogen evolution from the photocatalytic overall water splitting reaction.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...