Deciphering the selectivity of inhibitor MKC9989 towards residue K907 in IRE1α; a multiscale in silico approach
Abstract
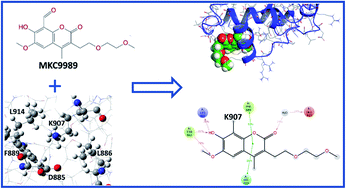
The selectivity of the ligand MKC9989, as inhibitor of the Inositol-Requiring Enzyme 1α (IRE1α) transmembrane kinase/ribonuclease protein, towards the residue K907 in the context of Schiff base formation, has been investigated by employing an array of in silico techniques including Multi-Conformation Continuum Electrostatics (MCCE) simulations, Quantum Mechanics/Molecular Mechanics (QM/MM) calculations, covalent docking, and Molecular Dynamics (MD) simulations. According to the MCCE results, K907 displays the lowest pKa value among all 23 lysine residues in IRE1α. The MMCE simulations also indicate a critical interaction between K907 and D885 within the hydrophobic pocket which increases significantly at low protein dielectric constants. The QM/MM calculations reveal a spontaneous proton transfer from K907 to D885, consistent with the low pKa value of K907. A Potential Energy Surface (PES) scan confirms the lack of energy barrier and transition state associated with this proton transfer reaction. Covalent docking and MD simulations verify that the protein pocket containing K907 can effectively stabilize the inhibitor by strong π–π and hydrogen bonding interactions. In addition, Radial Distribution Function (RDF) analysis shows that the imine group formed in the chemical reaction between MKC9989 and K907 is inaccessible to water molecules and thus the probability of imine hydrolysis is almost zero. The results of the current study explain the high selectivity of the MKC9989 inhibitor towards the K907 residue of IRE1α.
- This article is part of the themed collection: New Insights into Biomolecular Systems from Large-Scale Simulations


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...