Effect of film thickness and evaporation rate on co-evaporated SnSe thin films for photovoltaic applications
Abstract
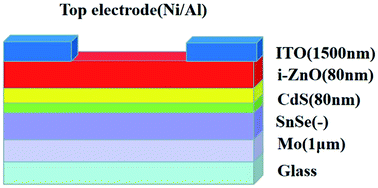
SnSe thin films were deposited by a co-evaporation method with different film thicknesses and evaporation rates. A device with a structure of soda-lime glass/Mo/SnSe/CdS/i-ZnO/ITO/Ni/Al was fabricated. Device efficiency was improved from 0.18% to 1.02% by a film thickness of 1.3 μm and evaporation rate of 2.5 Å S−1 via augmentation of short-circuit current density and open-circuit voltage. Properties (electrical, optical, structural) and scanning electron microscopy measurements were compared for samples. A SnSe thin-film solar cell prepared with a film thickness of 1.3 μm and evaporation rate of 2.5 Å S−1 had the highest electron mobility, better crystalline properties, and larger grain size compared with the other solar cells prepared. These data can be used to guide growth of high-quality SnSe thin films, and contribute to development of efficient SnSe thin-film solar cells using an evaporation-based method.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...