Ascorbic acid stabilised copper nanoclusters as fluorescent sensors for detection of quercetin
Abstract
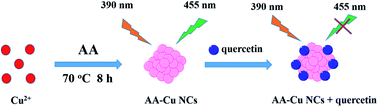
In this report, green-emitting fluorescence copper nanoclusters (Cu NCs) were synthesized using ascorbic acid as reducing agent and protecting agent. The ascorbic acid capped Cu NCs (AA-Cu NCs) were characterized using fluorescence spectroscopy, UV-vis absorption spectroscopy, Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR), Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). The analysis data demonstrated that the AA-Cu NCs were highly dispersed with an average diameter of 2 nm. The as-prepared Cu NCs possessed good water solubility, excellent photostability and displayed excitation-dependent fluorescence characteristics. More importantly, the fluorescence intensity of AA-Cu NCs was linearly quenched in the presence of quercetin from 0.7 to 50 μM and the detection limit (LOD) was 0.19 μM. Finally, the fluorescence sensor was successfully employed to detect quercetin in bovine serum samples.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...