Coupling hydrophilic interaction chromatography materials with immobilized Fe3+ for phosphopeptide and glycopeptide enrichment and separation†
Abstract
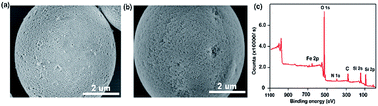
Simultaneous profiling of protein phosphorylation and glycosylation is very important to elucidate the bio-functions of these proteins. However, simultaneous enrichment of glyco- and phosphopeptides is the bottleneck in proteomics because of the low abundance of these species and ion suppression from non-modified peptides in mass spectrometry (MS). In this study, Fe3+ immobilized hydrophilic interaction chromatography (HILIC) materials (termed polySD-SiO2, recently reported in our lab) and polySD-SiO2 in the HILIC mode were employed for the simultaneous enrichment and subsequent separation of glyco- and phosphopeptides. The Fe3+ immobilized polySD-SiO2 could selectively enrich glycopeptides and phosphopeptides and the co-enriched peptides were further fractionated with polySD-SiO2 in the HILIC mode. With the established method, glyco- and phosphopeptides were well enriched and divided into two fractions even from tryptic digests of a-casein, fetuin and BSA at a molar ratio of 1 : 2 : 400. Application of the established method to HeLa cell lysate resulted in a total of 1903 phosphopeptides and 141 glycosylation sites. These results demonstrate that the established method could selectively and simultaneously enrich and fractionate glyco- and phosphopeptides from complex peptide mixtures.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...