Preparation of high-strength and lightweight microcellular polysulfone foam with a segregated CNT network for excellent electromagnetic shielding†
Abstract
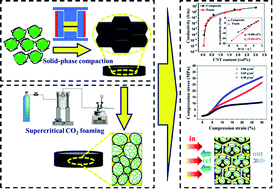
Fabrication of microcellular polymer composite foam based on high-performance plastic is a promising strategy for preparing the lightweight, high-strength and multifunctional materials. Herein, we proposed a facile and green method to prepare microcellular polysulfone/carbon nanotube (PSU/CNTs) composite foams with segregated structure by combining solid-phase milling and supercritical carbon dioxide (scCO2) foaming. The segregated PSU/CNTs foam with as low as 5.0 wt% CNT was provided with a good electrical conductivity of 5.2 S m−1 and an acceptable electromagnetic interference shielding effectiveness (EMI SE) of 23.7 dB, respectively. Moreover, the segregated PSU/CNT foam exhibited an ultralow percolation threshold of 0.06 vol%. An absorption-dominant shielding feature was observed for segregated PSU/CNT foam, which could be attributed to the synergistic effect of the perfect CNT networks and the microcellular structure in PSU domains. In addition, benefitting from the inherent properties of the PSU matrix, foam density dropped to 0.69 g cm−3, and the material still possessed a high specific compression strength of 38.8 MPa cm3 g−1. Therefore, our work provided an insight into the preparation of lightweight, high-strength and multifunctional materials that might have great potential applications in aerospace and military areas.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...