Preparation and properties of CF–Fe3O4–BN composite electromagnetic wave-absorbing materials
Abstract
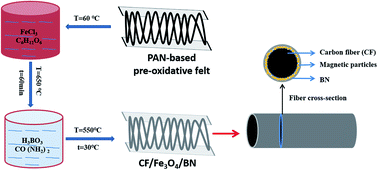
A three-layered electromagnetic (EM) wave-absorbing material was prepared by depositing a Fe3O4 and boron nitride (BN) coating onto the surface of a carbon fiber (CF) by in situ hybridization. The structure, chemical composition, morphology, high-temperature resistance, EM characteristics and EM wave absorption of the composite materials were analyzed. The composite materials contained CFs, and Fe3O4 was distributed along the axial direction of the fiber, whereas BN was found in the outermost coating layer. The proposed preparation method improved the oxidation resistance and EM wave absorption of CF. When the solubility of the metal salt was 20 g/100 ml, the decomposition temperature of the prepared CF/Fe3O4(3)/BN increased by more than 200 °C compared with that of CF/Fe3O4(3). The EM wave loss of less than −5 dB ranged within 8.8–18 GHz, and the effective EM wave-absorbing bandwidth (R < −10 dB) was 4.2 GHz (11.2–15.4 GHz). The prepared CF-based composite material had a lightweight structure, wide absorption band, and strong oxidation resistance. All these findings can serve as a reference for the study of other EM wave-absorbing materials.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...