Novel huperzine A based NMDA antagonists: insights from molecular docking, ADME/T and molecular dynamics simulation studies †
Abstract
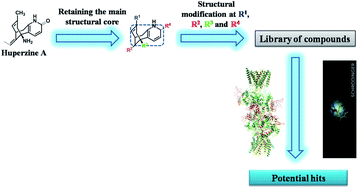
Huperzine A (HupA) is an alkaloidal natural product and drug isolated from Chinese herb Huperzia serrata, which is a potent selective anticholinesterase inhibitor. HupA has symptomatic, cognitive-enhancing and protective effect on neurons against amyloid beta-induced oxidative injury and antagonizing N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors by blocking the ion channels. The present study aimed to identify the docking, ADME/T and molecular dynamics simulation parameters of a library of 40 analogues which can correlate the binding affinity, conformational stability and selectivity of the ligands towards NMDA receptor through in silico approach. Glide molecular docking analysis was performed for the designed analogues to understand the binding mode and interactions. MD simulations were performed to explain the conformational stability and natural dynamics of the interaction in physiological environmental condition of protein–ligand complex affording a better understanding of chemical-scale interactions between HupA and its analogues with NMDA channel that could potentially benefit the development of new drugs for neurodegenerative diseases involving NMDA receptors.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...