Bubble-propelled micromotors based on hierarchical MnO2 wrapped carbon nanotube aggregates for dynamic removal of pollutants†
Abstract
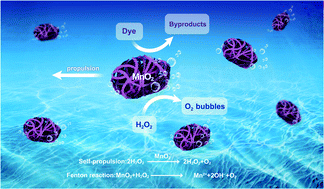
Water pollution is currently an urgent public health and environmental issue. Bubble-propelled micromotors might offer an effective approach for dealing with environmental contamination. Herein, we present the synthesis of multi-walled carbon nanotube (MWCNT)/manganese dioxide (MnO2) micromotors based on MWCNT aggregates as microscale templates by a simple one-step hydrothermal procedure. The morphology, composition, and structure of the obtained MWCNT/MnO2 micromotors were characterized in detail. The MnO2 nanoflakes formed a catalytic layer on the MWCNT backbone, which promoted effective bubble evolution and propulsion at remarkable speeds of 359.31 μm s−1. The bubble velocity could be modulated based on the loading of MnO2 nanoflakes. The rapid movement of these MWCNT/MnO2 catalytic micromotors resulted in a highly efficient moving adsorption platform, which considerably enhanced the effectiveness of water purification. Dynamic adsorption of organic dyes by the micromotors increased the degradation rate to approximately 4.8 times as high as that of their corresponding static counterparts. The adsorption isotherms and adsorption kinetics were also explored. The adsorption mechanism was well fitted by the Langmuir model, following pseudo-second-order kinetics. Thus, chemisorption of Congo red at the heterogeneous MnO2 wrapped microimotor surface was the rate determining step. The high propulsion speed and remarkable decontamination efficiency of the MWCNT/MnO2 micromotors indicate potential for environmental contamination applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...