Enhanced energy efficiency for the complete mineralization of diclofenac by self-sequential ultrasound enhanced ozonation
Abstract
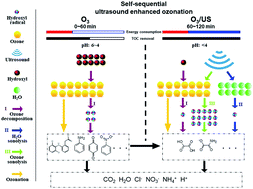
Diclofenac (DCF), an anti-biodegradable drug, needs to be post-treated after conventional biochemical treatment. In this paper, ultrasound enhanced ozonation (UEO) under different conditions was employed to degrade DCF. The results showed that DCF was completely degraded by UEO in 8 min and complete total organic carbon (TOC) removal occurred in 120 min. The generation of ˙OH via UEO could be achieved through ozone decomposition, H2O sonolysis, and ozone sonolysis, which contributed to the complete mineralization of DCF. The total amount of ˙OH produced by 200 kHz UEO was 3.8 times higher than that of single ozonation plus single sonolysis in 120 min. Typical persistent intermediates of DCF, such as oxalic acid and oxamic acid, could be efficiently degraded by UEO. It was found that 60 min ozonation followed by 60 min UEO had the best mineralization energy efficiency (MEE) (113 mg (kW h)−1) at the base of complete mineralization and there was one-third reduction in the total energy consumption compared to that for single UEO. Based on the analysis of the evolution index (EI), pH was selected as the best judgment index of self-sequential UEO for indicating the time point of ultrasound irradiation, which saves irradiation times for practical use.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...