Characterization of biocompatible pig skin collagen and application of collagen-based films for enzyme immobilization
Abstract
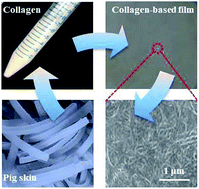
Based on the excellent biocompatibility of collagen, collagen was extracted from pig skin by acid-enzymatic method. The films were prepared by the self-aggregation behavior of collagen, and the catalase was immobilized by adsorption, cross-linking and embedding. The experiment investigated the effects of glutaraldehyde on the mechanical properties, external sensory properties, and denaturation temperature of the films. The results showed that self-aggregating material could maintain the triple helix structure of pig skin collagen. The self-aggregation treatment and cross-linking treatment can improve the mechanical properties to 53 MPa, while the glutaraldehyde cross-linking agent can increase the denaturation temperature of the pig skin collagen self-aggregating membrane by 20.35% to 84.48 °C. This means that its application to immobilized catalase has better stability. The comparison shows that the catalase immobilized by the adsorption method has strong activity and high operational stability, and the cross-linking agent glutaraldehyde and the initial enzyme concentration have a significant effect on the immobilization, and the activity can reach 175 U g−1. After 16 uses of the film, the catalase was completely inactivated. This study provides a reference for the preparation of a catalase sensor that can be used to detect hydrogen peroxide in food by a catalase sensor.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...