Synthesis, properties and photovoltaic performance in dye-sensitized solar cells of three meso-diphenylbacteriochlorins bearing a dual-function electron-donor†
Abstract
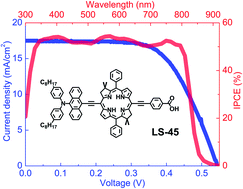
Bacteriochlorins are crucial to photosynthesis in bacteria. Studies of air-stable, meso-substituted bacteriochlorins are rare. We herein report the synthesis, properties, and photovoltaic performance of three new air-stable, meso-substituted bacteriochlorins bearing a dioctylfluorenylethyne (denoted as LS-17), a dioctylaminophenylethynylanthrylethyne (LS-43), and a diarylaminoanthrylethyne (LS-45) as the electron-donating groups. Among these LS-bacteriochlorins, LS-17 displays sharp UV-visible absorption bands whereas LS-43 and LS-45 give rise to broadened and red-shifted absorptions. Electrochemical and DFT results suggest that the first oxidation and reduction reactions of these bacteriochlorins are consistent with the formation of the cation and anion radicals, respectively. For dye-sensitized solar cell applications, photovoltaic performance of the LS-45 cell achieves an overall efficiency of 6.04% under one-sun irradiation.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...