Development of multiple reaction monitoring assay for quantification of carnosine in human plasma†
Abstract
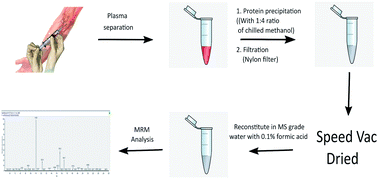
Carnosine, a histidine containing dipeptide, exerts beneficial effects by scavenging reactive carbonyl compounds (RCCs) that are implicated in pathogenesis of diabetes. However, the reduced carnosine levels may aggravate the severity of diabetes. The precise quantification of carnosine levels may serve as an indicator of pathophysiological state of diabetes. Therefore, we have developed a highly sensitive targeted multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) method for quantification of carnosine in human plasma samples. Various mass spectrometry parameters such as ionization of precursor, fragment abundance and stability, collision energy, tube lens offset voltage were optimized to develop a sensitive and robust assay. Using the optimized MRM assay, the lower limit of detection (LOD) and limit of quantification (LOQ) for carnosine were found to be 0.4 nM and 1.0 nM respectively. Standard curves were constructed ranging from 1.0 nM to 15.0 μM and the levels of carnosine in mice and human plasma were determined. Further, the MRM assay was extended to study carnosine hydrolyzing activity of human carnosinases, the serum carnosinase (CN1) and the cytosolic carnosinase (CN2). CN1 showed three folds higher activity than CN2. The MRM assay developed in this study is highly sensitive and can be used for basal plasma carnosine quantification, which can be developed as a novel marker for scavenging of RCCs in diabetes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...