Facile and accelerated production of RuO2 monolayers via a dual-step intercalation process†
Abstract
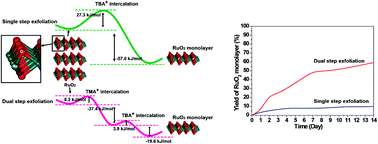
Tetrabutylammonium ions (TBA+) have commonly been used to exfoliate RuO2 into monolayers via ion exchange reactions. However, the low production yield of RuO2 exfoliation, which originates from the large molecular size of TBA+, limits wider utilisation of RuO2 monolayers in optoelectronic applications. We introduce a rapid and efficient dual-step exfoliation process beginning with intercalation of small organic molecules (tetramethylammonium ions) into RuO2, which is followed by the addition of TBA+ as a second intercalant to realize RuO2 monolayer production. Our dual-step intercalation process increases the RuO2 monolayer exfoliation yield from 9.9% to 60% after 14 days. Density functional theory calculations reveal that the activation energy of dual-step intercalation is much lower than that of direct intercalation of TBA+ ions into the RuO2 structure. The experimental and theoretical results of dual-step intercalation suggest that it is a facile and general approach for the production of metal oxide monolayers, and could widen the use of metal oxide monolayer nanosheets.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...