Additive-assisted synthesis and optoelectronic properties of (CH3NH3)4Bi6I22†
Abstract
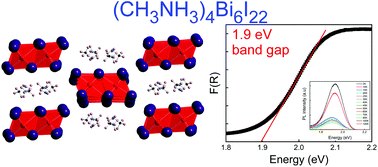
Hybrid organic–inorganic halides containing Bi and Sb generally exhibit higher stability and lower toxicity compared to Pb analogues. In this work, the synthesis, crystal and electronic structures and optical properties of a brand-new methylammonium bismuth iodide, (MA)4Bi6I22 (MA+ = CH3NH3+), are reported. Interestingly, we find that the presence of the HgI2 is necessary for the targeted preparation of (MA)4Bi6I22. (MA)4Bi6I22 contains isolated [Bi6I22]4− clusters made of six edge-sharing octahedral BiI6 units, which are separated by MA+ cations in its 0D crystal structure. A relatively low optical band gap of 1.9 eV was estimated for (MA)4Bi6I22 based on diffuse reflectance measurements. An intense photoluminescence peak emerges at 636 nm at low temperatures that supports the assigned band gap value. Electronic structure calculations show the presence of flat bands in the valence and conduction bands, consistent with the low-dimensional structure of (MA)4Bi6I22, and slightly indirect nature of the bandgap. Our findings suggest that the use of facilitator moieties such as HgI2 may provide a pathway to obtaining alternative methylammonium bismuth iodides to (MA)3Bi2I9.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...