Amphiphobic polyHIPEs with pH-triggered transition to hydrophilicity–oleophobicity for the controlled removal of water from oil–water mixtures†
Abstract
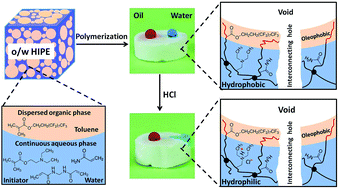
While emulsion-templated porous polymers (polyHIPEs) with pH-controlled wetting behaviours are advantageous for the removal of oils from oil–water mixtures, they are easily clogged by oils and are not suitable for separating mixtures consisting of a small amount of water and a large amount of oils. Herein, we report the fabrication of amphiphobic polyHIPEs from high internal phase emulsions via simultaneous solution polymerization and interface-induced polymerization. After pH adjustment with an HCl solution, the amphiphobicity of the polyHIPEs was transformed into hydrophilicity–oleophobicity, which enabled water to be selectively absorbed and separated from oil–water mixtures, and the pH-triggered transition achieved the separation in a controlled manner. Moreover, the absorption was realized in a continuous manner under an external pressure provided by a pump. The resulting hydrophilic–oleophobic polyHIPEs also absorbed water from emulsified oil–water mixtures (emulsions). The pH-triggered transition from amphiphobicity to hydrophilicity–oleophobicity and the selective absorption of water from oil–water mixtures in a continuous manner make the polyHIPEs excellent candidates for the controlled removal of water from oil–water mixtures.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...