Secondary structure drives self-assembly in weakly segregated globular protein–rod block copolymers†
Abstract
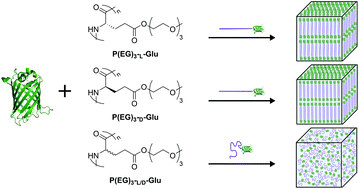
Protein–polymer bioconjugates represent a class of materials that integrate protein functionality with polymer material properties and block copolymer self-assembly. To investigate the effect of polymer block secondary structure and chirality on self-assembly of globular protein–helix diblock copolymers, four types of bioconjugates consisting of a poly(amino acid) and enhanced green fluorescent protein (eGFP) were synthesized and compared: two homochiral, α-helix-forming bioconjugates incorporating either L- or D-type poly(amino acids), a 1 : 1 blend of the L- and D-type bioconjugates, and a bioconjugate incorporating structureless, achiral poly(amino acids). Poly(amino acids) (PAAs) were synthesized via N-carboxy anhydride (NCA) polymerization, and PAAs were conjugated to eGFP via native chemical ligation. All bioconjugates with a helical block self-assembled into lamellae at all concentrations measured (20 to 60 wt%). In contrast, the random copolymer of L- and D-type monomers did not self-assemble at any concentration or temperature. This was shown to be an effect of a non-repulsive interaction between the flexible PAA and the eGFP blocks, which is strong enough to affect the protonation state of the eGFP chromophore in water. Therefore, secondary structure of the polymer block can modulate the effective segregation strength between blocks and drive self-assembly even in systems with non-repulsive blocks.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...