Curcumin–polymer conjugates with dynamic boronic acid ester linkages for selective killing of cancer cells†
Abstract
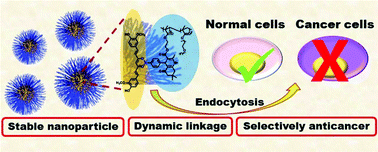
The poor water-solubility of curcumin limits the broad applications of this promising traditional herb. In this study, we developed a strategy to prepare curcumin–polymer conjugates with a dynamic covalent linkage. A phenylboronic acid (PBA)-containing monomer was synthesized via the Hantzsch reaction. This monomer was then copolymerized with a water-soluble monomer through radical polymerization to obtain a water-soluble copolymer. Curcumin was included in this copolymer via covalent linkage between the PBA group in the polymer and 1,3-diketone group in curcumin. The resulting curcumin–polymer conjugate formed stable nanoparticles at pH ∼ 7.4 that quickly decomposed at pH ∼ 5.5. Further, it was found that the curcumin–polymer conjugates could selectively kill different cancer cells, which illustrates the potential of this curcumin–polymer conjugate for cancer therapy. This report is the first to describe a synthetic strategy for curcumin–polymer conjugates involving a dynamic linkage between PBA and curcumin. Thus, the applicability of PBA-containing polymers has been expanded to deliver curcumin for therapeutic applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...