The effects of aloe emodin-mediated antimicrobial photodynamic therapy on drug-sensitive and resistant Candida albicans
Abstract
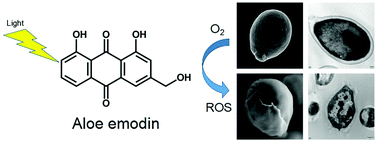
The extensive and repetitive use of antifungal drugs has led to the development of drug-resistant Candida albicans. Antimicrobial photodynamic therapy (aPDT) has received considerable attention as an emerging and promising approach to combat drug-resistant microbes. This study evaluated the photodynamic effects mediated by aloe emodin (AE), a natural compound isolated from Aloe vera and Rheum palmatum, on azole-sensitive and azole-resistant C. albicans in vitro. AE exhibited no significant dark toxicity, but in the presence of light, effectively inactivated C. albicans cells in a concentration-dependent manner. The uptake of AE by fungal cells was investigated by confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM), and the results showed that AE possessed stronger ability to enter into C. albicans cells following light irradiation. Transmission electron microscopy analysis suggested that AE-mediated aPDT could induce damage to the cell wall, cytoplasm, and nucleus. Damage to the surface of C. albicans was observed by scanning electron microscopy. These results suggest that AE is a potential PS for use in aPDT of drug-resistant C. albicans strains, and AE-mediated aPDT shows promise as an antifungal treatment.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...