Arylation of indoles using cyclohexanones dually-catalyzed by niobic acid and palladium-on-carbons†
Abstract
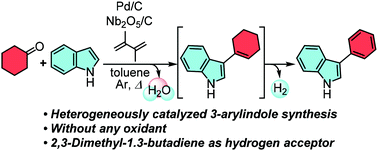
3-Arylindoles were easily constructed from indoles and cyclohexanone derivatives using a combination of catalytic niobic acid-on-carbon (Nb2O5/C) and palladium-on-carbon (Pd/C) under heating conditions without any oxidants. The Lewis acidic Nb2O5/C promoted the nucleophilic addition of indoles to the cyclohexanones, and the subsequent dehydration and Pd/C-catalyzed dehydrogenation produced the 3-arylindoles. The additive 2,3-dimethyl-1,3-butadiene worked as a hydrogen acceptor to facilitate the dehydrogenation step.
- This article is part of the themed collections: Synthetic methodology in OBC and Catalysis & biocatalysis in OBC


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...