The phosphorylation mechanism of mevalonate diphosphate decarboxylase: a QM/MM study†
Abstract
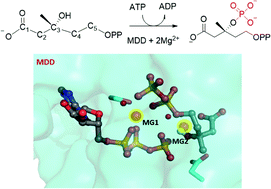
Mevalonate diphosphate decarboxylase (MDD) catalyses a crucial step of the mevalonate pathway via Mg2+-ATP-dependent phosphorylation and decarboxylation reactions to ultimately produce isopentenyl diphosphate, the precursor of isoprenoids, which is essential to bacterial functions and provides ideal building blocks for the biosynthesis of isopentenols. However, the metal ion(s) in MDD has not been unambiguously resolved, which limits the understanding of the catalytic mechanism and the exploitation of enzymes for the development of antibacterial therapies or the mevalonate metabolic pathway for the biosynthesis of biofuels. Here by analogizing structurally related kinases and molecular dynamics simulations, we constructed a model of the MDD–substrate–ATP-Mg2+ complex and proposed that MDD requires two Mg2+ ions for maintaining a catalytically active conformation. Subsequent QM/MM studies indicate that MDD catalyses the phosphorylation of its substrate mevalonate diphosphate (MVAPP) via a direct phosphorylation reaction, instead of the previously assumed catalytic base mechanism. The results here would shed light on the active conformation of MDD-related enzymes and their catalytic mechanisms and therefore be useful for developing novel antimicrobial therapies or reconstructing mevalonate metabolic pathways for the biosynthesis of biofuels.
- This article is part of the themed collections: Catalysis & biocatalysis in OBC and Mechanistic, computational & physical organic chemistry in OBC


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...