Oxygenated functional group-engaged electroless deposition of ligand-free silver nanoparticles on porous carbon for efficient electrochemical non-enzymatic H2O2 detection†
Abstract
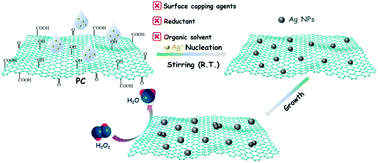
The construction of metal–carbon nanostructures with enhanced performances using traditional methods, such as pyrolysis, photolysis, impregnation–reduction, etc., generally requires additional energy input, reducing agents and capping ligands, which inevitably increase the manufacturing cost and environmental pollution. Herein, a novel one-step substrate-induced electroless deposition (SIED) strategy is developed to synthesize ligand-free Ag NPs supported on porous carbon (PC) (Ag/PC). The PC matrix enriched with oxygenated functional groups has a low work function and thus a low redox potential compared to that of Ag+ ions, which induces the auto-reduction of Ag+ ions to Ag NPs. The as-synthesized Ag/PC-6 modified electrode can be used as an excellent nonenzymatic H2O2 sensor with a broad linear range of 0.001–20 mM, a low detection limit of 0.729 μM (S/N = 3), and a high response sensitivity of 226.9 μA mM−1 cm−2, outperforming most of the reported sensor materials. Moreover, this electrode can be applied to detect trace amounts of H2O2 in juice and milk samples below the permitted residual level in food packaging and the recovery of H2O2 is 99.6% in blood serum (10%) with good reproducibility. This study proposes an efficient approach for synthesizing a highly active supported Ag electrocatalyst, which shows significant potential for practical applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...