A novel fluorescent covalent organic framework containing boric acid groups for selective capture and sensing of cis-diol molecules†
Abstract
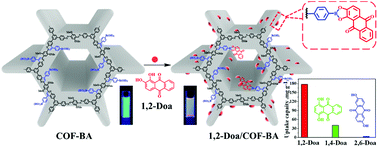
Owing to specific formation of five-membered or six-membered cyclic esters between boric acid groups and cis-diol molecules, boric acid bearing fluorescent materials can not only selectively capture but also specifically identify cis-diol substances. In this work, a novel covalent organic framework containing boric acid groups (COF-BA) was prepared through post-modification via the aza-Diels–Alder cycloaddition reaction. COF-BA with good stability, a permanent pore structure, a high specific surface area (606 m2 g−1) and a uniform pore size (2.59 nm) exhibited unique selectivity toward the cis-diol guest molecule 1,2-dihydroxyanthracene-9,10-dione (1,2-Doa) with a high adsorption capacity of 177.95 mg g−1. However, as for the isomers of 1,2-Doa (1,4-dihydroxyanthracene-9,10-dione and 2,6-dihydroxyanthracene-9,10-dione), the corresponding uptake capacities are distinctively decreased to 40.86 mg g−1 and 3.05 mg g−1, respectively. It is worth noting that the COF-BA can be recovered and recycled. Moreover, because the formation of the quinoline enhanced the conjugation effect of the COF skeleton, it was unexpectedly found that COF-BA possessed an intrinsic fluorescence property and could be used as an optical sensor for 1,2-Doa.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...