End-capped group manipulation of indacenodithienothiophene-based non-fullerene small molecule acceptors for efficient organic solar cells†
Abstract
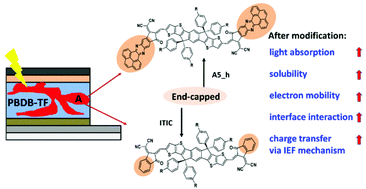
As the key component of organic solar cells (OSCs), the acceptor plays key roles in determining the power conversion efficiency (PCE). Based on the famous non-fullerene acceptor ITIC, a series of acceptors (A1–A5) were designed by introducing fused-ring units (phenanthrene, pyrene, benzopyrazine, dibenzo[a,c]phenazine, and phenanthro[4,5-abc]phenazine) as the end groups. Theoretical calculations showed that A1–A5 display improved solubility and redshifted absorption spectra compared with ITIC. More importantly, the newly designed acceptors exhibit much higher electron mobility, where the electron mobility of A5_h (similar to A5 but with the same hexyl side chain as ITIC) is about four orders of magnitude larger than that of ITIC. The computed binding energies of the donor PBDB-TF with the acceptor ITIC and A5_h are −2.52 eV and −3.75 eV, indicating much stronger interface interactions in PBDB-TF/A5_h. In terms of charge-transfer (CT) mechanism, we found that both PBDB-TF/ITIC and PBDB-TF/A5_h can generate CT states through direct excitation and hot excitons, meanwhile there exist more opportunities of producing CT states via the intermolecular electric field (IEF) mechanism in PBDB-TF/A5_h. Our results not only offer a set of promising ITIC-based acceptors, but also provide new insights into the donor/acceptor interface properties, which are closely related to the PCE of OSCs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...