Tailoring molecular interactions between microporous polymers in high performance mixed matrix membranes for gas separations†
Abstract
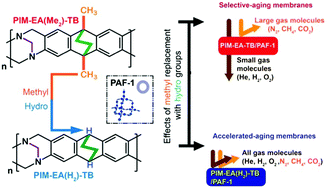
Membranes are crucial to lowering the huge energy costs of chemical separations. Whilst some promising polymers demonstrate excellent transport properties, problems of plasticisation and physical aging due to mobile polymer chains, amongst others, prevent their exploitation in membranes for industrial separations. Here we reveal that molecular interactions between a polymer of intrinsic microporosity (PIM) matrix and a porous aromatic framework additive (PAF-1) can simultaneously address plasticisation and physical aging whilst also increasing gas transport selectivity. Extensive spectroscopic characterisation and control experiments involving two near-identical PIMs, one with methyl groups (PIM-EA(Me2)-TB) and one without (PIM-EA(H2)-TB), directly confirm the key molecular interaction as the adsoprtion of methyl groups from the PIM matrix into the nanopores of the PAF. This interaction reduced physical aging by 50%, suppressed polymer chain mobilities at high pressure and increased H2 selectivity over larger gases such as CH4 and N2.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...