Carbon nano-onion-powered optically transparent and economical dye-sensitized solar cells†
Abstract
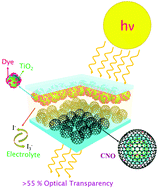
The integration of dye-sensitized solar cells (DSSCs) with building roof panels, windows, and various decorative outdoor installations is presently an important research topic for their immediate commercialization potential because of their power generation capability, sustainability, and aesthetic appearance. For industrial applications, Pt counter electrodes (CEs) need to be replaced with Pt-free CEs because of their limited sources and cost. An ideal CE should be economical, abundant, and have excellent electrochemical stability and activity, with easy processing in bulk. As an alternative practical CE, we introduce for the first time a carbon nano-onion (CNO)-based CE for transparent DSSCs. We developed a simple, energy-efficient one-step synthesis technique for fabricating high-quality CNOs in bulk quantities without any sophisticated instrumentation and expensive nanodiamond precursors. CNO CEs proved to be promising in terms of optical transparency, reasonable electrochemical redox activity for the I−/I3− redox couple, and exchange current density comparable to Pt CEs. CNO-powered DSSCs demonstrated an optical transparency of >55% with a significant solar energy conversion efficiency of 5.17%. The intrinsic hydrophilicity of the as-synthesized CNO eliminates the use of a binder or an additive, unlike in the case of other carbon allotropes. Our results demonstrate the possibility of using CNO-based CEs as promising substitutes for scarce and expensive Pt-based CEs for low-cost DSSCs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...