Solid-state thiolate-stabilized copper nanoclusters with ultrahigh photoluminescence quantum yield for white light-emitting devices†
Abstract
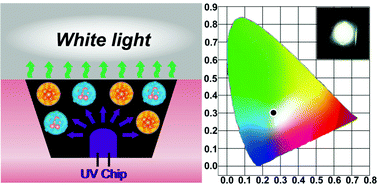
As a new emerging candidate for solid-state phosphors, copper nanoclusters (CuNCs) have gained tremendous interest in the field of white light-emitting devices (WLEDs). However, their further applications are impeded by the low photoluminescence quantum yield (PLQY) and poor emission color tunability of CuNCs. This work demonstrates the synthesis of cyan and orange emitting CuNCs, and their combination as color conversion phosphors in WLEDs. The cyan and orange emitting CuNCs were prepared employing 2-mercapto-1-methylimidazole (MMI) and N-acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC), respectively, as stabilizing-cum-reducing agents. The dispersions of MMI-CuNCs and NAC-CuNCs are weakly emissive. However, after processing into powders, they both possess ultrahigh PLQYs (45.2% for MMI-CuNCs, and 64.6% for NAC-CuNCs) owing to the effect of aggregation-induced emission (AIE). All-CuNC based WLEDs are then designed and developed using powdered MMI-CuNC and NAC-CuNC samples on commercially available 365 nm GaN LED chips. They display acceptable white light characteristics with a Commission Internationale de l'Eclairage coordinate value and color rendering index of (0.26, 0.30) and 83, respectively. We believe that these cost-effective and eco-friendly CuNCs with interesting AIE properties will vigorously promote the development of high-quality WLEDs for commercial applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...