Boosting the energy density of supercapacitors by encapsulating a multi-shelled zinc–cobalt-selenide hollow nanosphere cathode and a yolk–double shell cobalt–iron-selenide hollow nanosphere anode in a graphene network†
Abstract
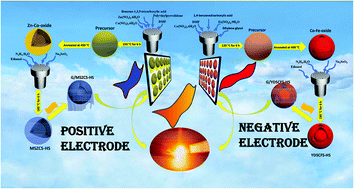
The practical exploration of electrode materials with complex hollow structures is of considerable significance in energy storage applications. Mixed-metal selenides (MMSs) with favorable architectures emerge as new electrode materials for supercapacitor (SC) applications owing to their excellent conductivity. Herein, a facile and effective metal–organic framework (MOF)-derived strategy is introduced to encapsulate multi-shelled zinc–cobalt-selenide hollow nanosphere positive and yolk–double shell cobalt–iron-selenide hollow nanosphere negative electrode materials with controlled shell numbers in a graphene network (denoted as G/MSZCS-HS and G/YDSCFS-HS, respectively) for SC applications. Due to the considerable electrical conductivity and unique structures of both electrodes, the G/MSZCS-HS positive and G/YDSCFS-HS negative electrodes exhibit remarkable capacities (∼376.75 mA h g−1 and 293.1 mA h g−1, respectively, at 2 A g−1), superior rate performances (83.4% and 74%, respectively), and an excellent cyclability (96.8% and 92.9%, respectively). Furthermore, an asymmetric device (G/MSZCS-HS//G/YDSCFS-HS) has been fabricated with the ability to deliver an exceptional energy density (126.3 W h kg−1 at 902.15 W kg−1), high robustness of 91.7%, and a reasonable capacity of 140.3 mA h g−1.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...