Trigger-responsive engineered-nanocarriers and image-guided theranostics for rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
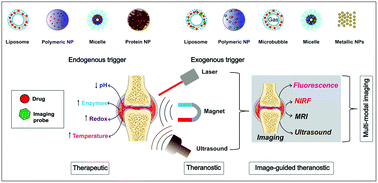
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA), one of the leading causes of disability due to progressive autoimmune destruction of synovial joints, affects ∼1% of the global population. Standard therapy helps in reducing inflammation and delaying the progression of RA but is limited by non-responsiveness on long-term use and several side-effects. The conventional nanocarriers (CNCs), to some extent, minimize toxicity associated with free drug administration while improving the therapeutic efficacy. However, the uncontrolled release of the encapsulated drug even at off-targeted organs limits the application of CNCs. To overcome these challenges, trigger-responsive engineered nanocarriers (ENCs) have been recently explored for RA treatment. Unlike CNCs, ENCs enable precise control over on-demand drug release due to endogenous triggers in arthritic paws like pH, enzyme level, oxidative stress, or exogenously applied triggers like near-infrared light, magnetic field, ultrasonic waves, etc. As the trigger is selectively applied to the inflamed joint, it potentially reduces toxicity at off-target locations. Moreover, ENCs have been strategically coupled with imaging probe(s) for simultaneous monitoring of ENCs inside the body and facilitate an ‘image-guided-co-trigger’ for site-specific action in arthritic paws. In this review, the progress made in recently emerging ‘trigger-responsive’ and ‘image-guided theranostics’ ENCs for RA treatment has been explored with emphasis on the design strategies, mechanism, current status, challenges, and translational perspectives.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Recent Review Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...