The surface plasmonic welding of silver nanowires via intense pulsed light irradiation combined with NIR for flexible transparent conductive films†
Abstract
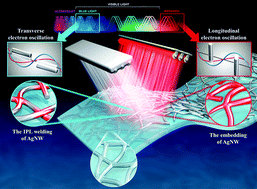
In this work, surface plasmonic welding of silver nanowires (AgNWs) by intense pulse light (IPL) combined with NIR was investigated. AgNWs were coated on a flexible PET (polyethylene terephthalate) substrate using a bar-coater. The coated AgNW films were welded at room temperature and under ambient conditions by white IPL from a xenon lamp, assisted with light from a UV-C (ultraviolet C) and NIR (near infra-red) lamp using an in-house multi-wavelength IPL welding system. In order to investigate the welding mechanism, in situ monitoring with a Wheatstone bridge electrical circuit was performed. The sheet resistance changes of AgNW films during the welding process were monitored under various IPL conditions (e.g. light energy and on-time) with and without UV-C and NIR light irradiation. The microstructure of the welded AgNW film and the interface between the AgNW film and the PET substrate were observed using a scanning electron microscope (SEM) and transmission electron microscope (TEM). COMSOL multi-physics simulations were conducted and compared with the in situ monitoring results to discuss the in-depth mechanism of the IPL welding of AgNWs and its dependence on the wavelength of light. From this study, the optimal IPL welding conditions and appropriate wavelength were suggested, and the optimized IPL welding process could produce AgNW film with a lower sheet resistance (45.2 Ω sq−1) and high transparency (96.65%) without damaging the PET substrate.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...