A novel αvβ3 integrin-targeted NIR-II nanoprobe for multimodal imaging-guided photothermal therapy of tumors in vivo†
Abstract
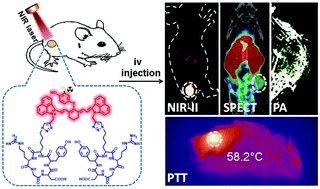
Developing novel small-molecule-based probes with both deep tissue imaging and therapeutic functions is highly significant in cancer diagnosis and treatment. Herein, we report a novel second near-infrared (NIR-II) fluorescent probe QT-RGD constructed with a NIR-II emissive organic fluorophore and two cyclic-(arginine-glycine-aspartic acid) (cRGD) peptides that can specifically bind to the tumor-associated αvβ3 integrin for accurate tumor diagnosis and targeting therapy. The isotopic 125I-labeled probe exhibited great tumor targeting ability and emitted intensive NIR-II/photoacoustic (PA)/single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) signals, which allows specific and sensitive multimodal visualization of tumors in vivo. More notably, this probe could also be applied for effective imaging-guided photothermal therapy (PTT) of tumors in mouse models owing to its prominent photothermal conversion efficiency and excellent photothermal stability. We thus envision that our work which unveils a combination of NIR-II/PA/SPECT imaging and PTT would offer a valuable means of improving tumor diagnostic accuracy as well as therapeutic efficacy.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2020 Nanoscale HOT Article Collection


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...