Large-sized graphene oxide synergistically enhances parenchymal hepatocyte IL-6 expression monitored by dynamic imaging†
Abstract
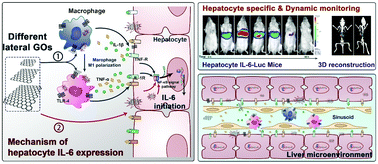
Graphene oxides (GOs) have received significant attention as emerging biomedical materials due to their special properties. The application of GOs in biological systems has raised considerable concern about their hepatotoxicity, however their biological effects on parenchymal hepatocytes remain unclear, despite the fact that GOs have shown size-dependent interactions with immunocytes in the liver. Herein we chose pleiotropic cytokine IL-6 as the model parameter to investigate inflammation responses upon exposure to GOs. An early and sensitive reporter mouse model was constructed, allowing non-invasive and longitudinal imaging of parenchymal hepatocyte IL-6 expressions. GOs of various lateral dimensions were assessed by using the reporter mice. The results demonstrated that large-sized GOs (L-GO) induced much stronger IL-6 activation. A detailed analysis uncovered that L-GO induced ROS production and TLR-4 activation promoted macrophage polarization and secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-1β and TNF-α, activated via> the NF-κB signaling pathway, which in turn initiated the expression of IL-6 in hepatocytes. These in-depth investigations are expected to help modulate the inflammatory responses involved in hepatotoxicity and provide extended information to design sub-hepatic distribution and cell subset targeting by controlling the nanoparticle sizes.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...