Non-aqueous solution-processed phosphorene by controlled low-potential electrochemical exfoliation and thin film preparation†
Abstract
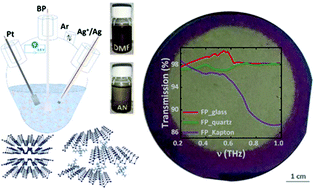
Black phosphorus (BP) in its monolayer form called phosphorene is thought of as a successor of graphene and is of great interest for (opto)electronic applications. A quantitative and scalable method for the synthesis of (mono-)few-layer phosphorene has been an outstanding challenge due to the process irreproducibility and environmental degradation capability of the BP. Here, we report a facile controlled electrochemical exfoliation method for the preparation of a few-layer phosphorene (FP) with nearly 100% yield. Our approach relies on the low-potential influence in anhydrous and oxygen-free low-boiling acetonitrile (AN) and N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF) using alkylammonium ions. Herein, intercalation of positive ions into BP interlayers occurred with a minimum potential of −2.95 V in DMF and −2.85 V in AN and the non-damaging and highly accurate electrochemical exfoliation lasted at −3.8 V. A variety of analytical methods have revealed that in particular DMF-based exfoliation results in high-quality phosphorene of 1–5 layers with good crystallinity and lateral sizes up to tens of micrometers. Moreover, assurance of the oxygen- and water-free environment allowed us to minimize the surface oxidation of BP and, consequently, exfoliated phosphorene. We pioneer an effective and reproducible printing transfer of electrochemically exfoliated phosphorene films onto various flexible and rigid substrates. The surfactant-free process of exfoliation allowed assembly and transfer of thin films based on FP. The phosphorene-based films characterized as direct gap semiconductors have a layer-number-dependent bandgap with a tuning range larger than that of other 2D materials. We show that on varying the films’ thickness, it is possible to modify their optical properties, which is a significant advantage for compact and switchable optoelectronic components.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...