Effective removal of inorganic and organic heavy metal pollutants with poly(amino acid)-based micromotors†
Abstract
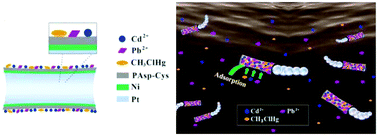
The increasing extent of heavy metal pollution all over the world has resulted in many serious environmental and public health problems. To solve these problems, effective technologies for water treatment are urgently needed. Recent efforts have focused on the development of self-driven micro/nanomotors for eliminating inorganic and organic pollutants in an aqueous system. These synthetic micro/nanomotors can increase mass transfer through the transportation of reactive species, leading to higher decontamination rates. Here, we report a surface-tunable poly(amino acid) (PAA)-based micromotor. The property of the outer layer can be adjusted by changing the type and proportion of amino acids according to real requirements. Three kinds of micromotors are fabricated, which consist of a microtube composed of PAAs (i.e., polyaspartic acid (PAsp), polycysteine (PCys) or a copolymer of both (PAsp-Cys)), a thin Ni intermediate layer, and a Pt inner layer. Due to the presence of various side-chain functional groups (e.g., amino, carboxyl, and sulfhydryl) on the surface of the poly(amino acid)s, these micromotors can be used as effective scavengers for the removal of heavy metals (i.e., Cd2+, Pb2+ and methylmercury). Compared with PAsp and PCys micromotors, the PAsp-Cys micromotor shows good acid resistance and can simultaneously adsorb various kinds of heavy metals with high removal efficiency. The outer layer of the surface-tunable micromotor has good biocompatibility and adsorption efficiency, which holds considerable promise for environmental and biomedical applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...