Natural products in agarwood and Aquilaria plants: chemistry, biological activities and biosynthesis†
Abstract
Covering: Up to the end of 2019.
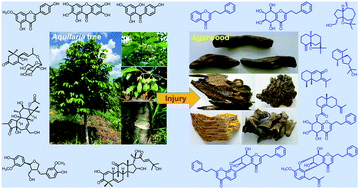
Agarwood is a resinous portion of Aquilaria trees, which is formed in response to environmental stress factors such as physical injury or microbial attack. It is very sought-after among the natural incenses, as well as for its medicinal properties in traditional Chinese and Ayurvedic medicine. Interestingly, the chemical constituents of agarwood and healthy Aquilaria trees are quite different. Sesquiterpenes and 2-(2-phenethyl)chromones with diverse scaffolds commonly accumulate in agarwood. Similar structures have rarely been reported from the original trees that mainly contain flavonoids, benzophenones, xanthones, lignans, simple phenolic compounds, megastigmanes, diterpenoids, triterpenoids, steroids, alkaloids, etc. This review summarizes the chemical constituents and biological activities both in agarwood and Aquilaria trees, and their biosynthesis is discussed in order to give a comprehensive overview of the research progress on agarwood.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...