Comparison of molecularly imprinted plasmonic nanosensor performances for bacteriophage detection†
Abstract
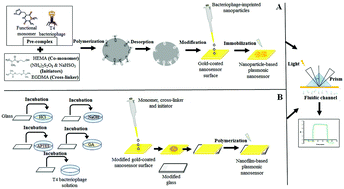
Contamination of drinking and surface waters with microorganisms is a problem that attracts attention because it threatens human health. One of the microorganisms that determine fecal contamination in water is a bacteriophage that infects coliform bacteria. A fast, real-time, sensitive, and low-cost alternative method is the nanosensor system for microorganism detection. This study aimed to develop a surface plasmon resonance nanosensor for the detection of T4 bacteriophages using nanoparticle- and nanofilm-based polymers. In this context, nanoparticle and nanofilm-based imprinted polymers were synthesized to develop nanosensors, and their efficacy was compared in fecal pollution determination in water. Following the characterization studies, nanoparticle and nanofilm-based plasmonic nanosensors were used to carry out kinetic studies in the 1 × 104–4 × 106 pfu mL−1 concentration range in buffer, sea, and tap water sample solutions. Reusability and selectivity studies were also performed. According to the results, the nanoparticle and nanofilm-based plasmonic nanosensors could measure with 98% and 81% precision, respectively. The limit of detection values was calculated as 6 × 103 pfu mL−1 and 8 × 103 pfu mL−1 for the nanoparticle and the nanofilm-based plasmonic nanosensors, respectively. In addition, the recovery value of the nanoparticle-based plasmonic nanosensor was calculated as 91–96%, while the nanofilm-based plasmonic nanosensor was calculated as 85–90% in tap and seawater samples. All results showed that both plasmonic nanosensors could detect with high selectivity, but the nanoparticle-based plasmonic nanosensor has higher sensitivity than the nanofilm-based plasmonic nanosensor.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...